
Preliminary Results of an AI Classifier to Diagnose Cervical Precancer on Real-World Data
To provide descriptive statistics of AVE’s performance on 3 cervical cancer projects in China: 1 NIH clinical trial and 2 screening camps.

To provide descriptive statistics of AVE’s performance on 3 cervical cancer projects in China: 1 NIH clinical trial and 2 screening camps.
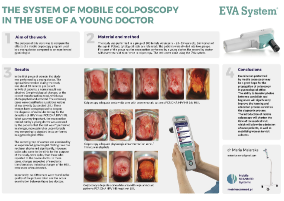
The purpose of this work was to compare the effects of a mobile colposcopy program used by a young doctor compared to an experienced gynecologist.

To assess the feasibility of a live, telecolposcopy system in clinics serving high-risk populations. Of interest is to understand the feasibility of an integrated telecolposcopy solution from the perspectives of patient and provider acceptance in comparison to in-person oversight of an exam.
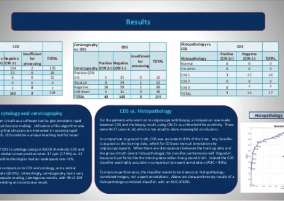
Demonstrate effectiveness of the first use of a prospective, real-time machine learning (ML) algorithm in a clinical setting.
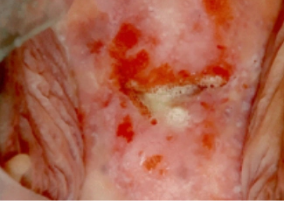
Logistical and economic issues make traditional cytology-based cervical cancer screening challenging in developing countries. Alternative, cost-effective, screening strategies must be developed to screen millions of women in resource-poor countries such as Cambodia.
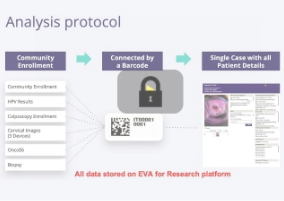
When running large trials, histopathology services are used to assess the state of a tissue. However, in many clinics in low resource settings there are large variations in quality of such services, specifically in biopsy processing and histopathological interpretation/assessment of images. Quality assurance (QA) is needed, but it involves physically mailing slides to a remote clinic. A telemedicine solution can address this challenge.

NOTE: Using the EVA System to visualize and document the instruction with the cervical cancer instructional apparatus.
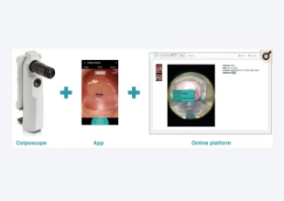
Abstract : A persistent challenge facing global health actors is ensuring that time-bound interventions are ultimately adopted and integrated into local health systems for long term health system strengthening and capacity building.